 |
 |
- Search
| Neonatal Med > Volume 26(3); 2019 > Article |
|
Abstract
Purpose
This study aimed to evaluate the clinical and radiologic findings suggestive of spontaneous intestinal perforation (SIP) in extremely-low-birth-weight infants (ELBWIs) with persistent gasless abdomen, and to investigate the usefulness of abdominal ultrasonography for the diagnosis of SIP.
Methods
In total, 22 infants with birth weights less than 1,000 g who showed persistent gasless abdomen on simple abdominal radiography were included. Perinatal, neonatal, and perioperative clinical findings were retrospectively reviewed, and the risk factors for intestinal perforation were evaluated. Abdominal sonographic findings suggestive of intestinal perforation were also identified, and postoperative short-term outcomes were evaluated.
Results
In total, eight of the 22 infants (36.4%) with gasless abdomen had SIP. The number of infants with patent ductus arteriosus who were treated with intravenous ibuprofen or indomethacin was significantly higher in the SIP group than in the non-SIP group (P<0.05). Greenish or red gastric residue, abdominal distension, or decreased bowel sound were more frequent in infants with SIP (P<0.05), in addition to gray or bluish discoloration of abdomen, suggestive of meconium peritonitis (P<0.05). Pneumoperitoneum on simple abdominal radiography was found in only one of the eight infants (12.5%) with SIP. Intramural echogenicity and echogenic extramural material on abdominal ultrasonography were exclusively observed in infants with SIP. Four infants (50%) with SIP died after surgical intervention.
Gasless abdomen has been defined as a state of scanty or invisible intestinal gas on simple abdominal radiography [1]. Until recently, the incidence of gasless abdomen in premature infants has not been well-documented. A recent study reported that 57 (11.5%) of 496 extremely-low-birth-weight infants (ELBWIs) with birth weight less than 1,000 g showed gasless abdomen on radiography, and 12 (21.1%) of them had been confirmed to have spontaneous intestinal perforation (SIP) [1]. However, the incidence of SIP in ELBWIs with gasless abdomen remains unclear. Several other studies have reported that gasless abdomen may commonly present in ELBWIs with SIP (52.0% to 67.0%) [1-6].
SIP is a common complication observed in ELBWIs with birth weight less than 1,000 g, and it has been described as a distinct clinical entity that differs from necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC), in terms of both clinical and histologic presentation [1,4,5]. Unlike NEC that accompanies radiologic hallmarks on simple abdominal radiography, such as pneumatosis intestinalis, or portal vein gas, and fixed bowel loop, SIP does not show distended, fixed bowel loops, pneumatosis intestinalis, or portal venous gas on abdominal radiography, and the most common radiological finding in infants with SIP has been gasless abdomen [1,4,6]. In addition, SIP associated with gasless abdomen in ELBWIs may occur without any signs suggestive of intestinal perforation, such as pneumoperitoneum, which can be found in only 33.3% to 50.0% of cases [4,6]. This low rate of intraperitoneal free air in SIP could be explained by the fact that perforation in SIP occurs as a more gradual process with slow spillage of meconium or bile-stained intraluminal material into the peritoneum rather than as a sudden event caused by rupture of subserosal cavity in NEC [1,4,6]. Moreover, intestinal structures other than the perforation site usually tend to be relatively well preserved [4,6]. Thus, it is often difficult to diagnose SIP in infants with gasless abdomen by simple abdominal radiography in the absence of pneumoperitoneum [2,7].
Given that the delayed treatment of SIP in ELBWIs owing to difficulty in early diagnosis may increase the likelihood of subsequent dismal outcomes, a more careful clinical and radiologic assessment is required if the gasless abdomen is persistently observed in these infants [3]. In this regard, previous studies have reported that abdominal ultrasonography had an important role in the early diagnosis of SIP in ELBWIs with gasless abdomen [1,7].
Thus, in this study, we intended to evaluate the clinical and radiologic findings for early diagnosis of SIP in ELBWIs with persistent gasless abdomen, and to determine the risk factors associated with SIP. We also aimed to evaluate the usefulness of abdominal ultrasonography for the diagnosis of SIP in ELBWIs with gasless abdomen.
This study included 22 ELBWIs with birth weight less than 1,000 g, whose simple abdominal radiography showed persistently gasless abdomen lasting for more than 3 days (Figure 1). All infants had been admitted to the neonatal intensive unit (NICU) of Dankook University Hospital between 2008 and 2015. Perinatal, neonatal, and perioperative clinical and radiologic findings were retrospectively reviewed and compared between infants without and with SIP, and the risk factors associated with SIP were determined. Postoperative neonatal outcomes were also evaluated. Infants with a perforation secondary to other etiologies such as congenital gastrointestinal anomalies or congenital meconium peritonitis were not included. All infants suspected of having clinical or radiological signs suggestive of intestinal perforation underwent surgical intervention. SIP was defined at laparotomy as the presence of isolated intestinal perforation surrounded by normal-appearing bowel and the absence of characteristic gross or microscopic features of NEC.
Abdominal ultrasonography was conducted in infants who showed gasless abdomen on simple abdominal radiography for at least 3 consecutive days or in infants with clinical symptoms suggestive of meconium peritonitis or intestinal perforation, such as gray or bluish abdominal discoloration and/or free air on simple abdominal radiography. Abdominal ultrasonography was performed in the NICU, and the findings were evaluated by a pediatric radiologist.
Statistical analysis was performed using SPSS version 23.0 (IBM Co., Armonk, NY, USA). Variables were compared between the SIP and non-SIP groups using the independent t-test, chisquare test, FisherŌĆÖs exact test, and Mann-Whitney U-test. P-values less than 0.05 were considered significant. This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board (IRB File No. DKUH 2019-05-025). Informed consent was waived by the board.
In total, eight of the 22 infants (36.4%) with gasless abdomen on simple abdominal radiography had SIP. Mean gestational age and mean birth weight did not significantly differ between infants without and with SIP (25.0┬▒1.0 weeks vs. 23.9┬▒1.6 weeks, 793.6┬▒143.9 g vs. 743.8┬▒166.6 g, respectively; P>0.05). The number of infants with patent ductus arteriosus (PDA) who were treated with intravenous ibuprofen or indomethacin was significantly higher in the SIP group (87.5%) than in the non-SIP group (42.9%; P<0.05). Indomethacin was administered in only one infant without SIP. Other perinatal and postnatal factors including twin pregnancy, premature rupture of membrane (>18 hours), maternal diabetes, complete dose of antenatal corticosteroid, respiratory distress syndrome treated with surfactant, bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD), use of postnatal dexamethasone for BPD, use of inotropics or hydrocortisone for hypotension, intraventricular hemorrhage greater than stage 2, periventricular leukomalacia, and retinopathy of prematurity (ROP) greater than stage 2 were not significantly different between infants without and with SIP (P>0.05). There were four cases of sepsis presumed to be temporally related to gasless abdomen, two (14.8%) in the non-SIP and two (20.0%) in the SIP groups, which was not significantly different (P>0.05). Enterococcus species and group B Streptococcus (GBS) were detected on blood culture in two infants with SIP, and Candida and Serratia species were detected in two infants without SIP. In-hospital death was not significantly different between the non-SIP and SIP groups (P>0.05). In addition, age of death and duration of hospital stay were not significant different between the non-SIP and SIP groups (P>0.05) (Table 1).
Trophic feedings before onset of gasless abdomen were performed in seven (50.0%) and five infants (62.5%) of the non-SIP and SIP groups, respectively (P>0.05), and breast feeding was performed in six (42.9%) and five infants (62.5%) of the non-SIP and SIP groups, respectively (P>0.05). Age of initiation of trophic feeding was not significantly different between the two groups (P>0.05). Greenish or red gastric residue, abdominal distension, or decreased bowel sound were more frequent in infants with SIP (P<005). In particular, gray or bluish discoloration of the abdomen suggesting meconium peritonitis was that observed in six infants (75%) of the SIP group, which was significantly more frequent compared to that observed in the two infants (14.3%) in the non-SIP group (P<0.05). Infants in the non-SIP group who had bluish discoloration of the abdomen did not reveal radiologic or clinical evidence that is attributable to NEC. The age of perforation in infants with SIP was 11.6┬▒4.4 days (Table 2).
Ages at which gasless abdomen was detected on simple abdominal radiography were 5.9┬▒4.7 and 7.3┬▒3.2 days of life in the non-SIP and SIP groups, respectively (P>0.05). The durations of gasless abdomen on simple abdominal radiography were 8.7┬▒6.8 and 8.3┬▒5.4 days of life in the non-SIP and SIP groups, respectively (P>0.05). Pneumoperitoneum on simple abdominal radiography was found in only one of the eight infants (12.5%) with SIP. Abdominal ultrasonography showed ascites or focal fluid collection in three infants (21.4%) in the non-SIP group; otherwise, the findings were mostly unremarkable. Meanwhile, abdominal ultrasonography of the infants in the SIP group showed bowel wall thickening (50.0%), intramural echogenicity (75.0%), and echogenic extramural material (50.0%; P <0.05); ascites or focal fluid collection was also detected in four infants (50%) in the SIP group (Table 3, Figure 2).
All infants with SIP had isolated focal intestinal perforations surrounded by a normal-appearing bowel (100%). Perforation occurred in the terminal ileum in five infants (62.5%); in the proximal ileum, in one infant (12.5%); in the transverse colon, in one infant (12.5%); and in the cecum, in one infant (12.5%). None of the surgical specimens were compatible with the gross or microscopic features of NEC. Primary peritoneal drainage was performed in three infants (37.5%), and primary laparotomy with resection of perforated segments of the intestine was performed in five infants (62.5%). All three infants treated with primary peritoneal drainage required salvage laparotomy. Four infants (50%; one who underwent primary peritoneal drainage [33.3%] and three who underwent primary laparotomy [60.0%]) died at 0, 4, 6, and 12 days after operation (Table 4). Three of them died owing to problems related to postoperative bleeding, and there was no additional neonatal death in the SIP group.
This study showed the clinical and radiological findings associated with SIP occurring in ELBWIs with persistent gasless abdomen on simple abdominal radiography. PDA treated with intravenous ibuprofen or indomethacin might be regarded as a significant risk factor associated with SIP in ELBWIs with gasless abdomen. Pneumoperitoneum was found in only one of the eight infants (12.5%) with SIP on simple abdominal radiography; abdominal ultrasonography in the non-SIP group showed ascites or focal fluid collection in three infants; the other findings were mostly unremarkable. Meanwhile, abdominal ultrasonography of infants in the SIP group exclusively showed findings suggestive of intestinal perforation such as intramural echogenicity (75.0%), echogenic extramural material (50.0%) and ascites (50%), with or without bowel wall thickening (50.0%). Thus, this study suggested that abdominal ultrasound might help detect intestinal perforation when SIP is suspected in ELBWIs with gasless abdomen.
Several causes of SIP in extremely premature infants have been suggested. Multifocal partial or complete defects of musculature in the intestinal muscular layer have been frequently observed in the histologic findings of SIP [8-12]. Thus, defects in the muscle layer owing to immaturity in premature infants might be considered as one of the causes of SIP. Additionally, ischemia caused by stress, hypoxia, and/or hypotension before or after birth may lead to disruptions in both musculature and mucosa followed by the regeneration of mucosa, which results in total or partial absence of musculature [13,14]. Thus, SIP occurs typically in the terminal ileum, also known as the ŌĆ£watershed zone,ŌĆØ which is vulnerable to ischemia [15,16]. In this study, similar to the results of previous studies, the most common perforation site was the terminal ileum. However, it is not fully understood whether perforation occurs in other parts of the intestine, such as the colon or proximal ileum, which have more blood supply, as well as in multiple sites.
SIP of the newborn occurs primarily in ELBWIs with an incidence of approximately 3% in this specific population [17-19]. The median age at presentation of SIP ranges from 7 to 15 days [4,15,19-22], which was 11.6┬▒4.4 days in this study. It is well-known that prostaglandin inhibitors such as indomethacin used for the treatment of PDA in premature infants could reduce blood flow to the intestinal tract and induce bowel wall ischemia, subsequently leading to SIP [4,23-25]. Combined with indomethacin for treating PDA, administration of glucocorticoids is commonly reported to be a risk factors for SIP, and exposure to both indomethacin and hydrocortisone in the first week of life might significantly increase the risk of SIP in very-low-birth-weight infants [26]. Moreover, a study reported that the use of ibuprofen could be related to the occurrence of SIP in premature infants [27]. Similarly, this study suggested that PDA treated with intravenous ibuprofen or indomethacin might be a risk factor associated with the occurrence of SIP. However, we were unable to investigate whether hydrocortisone might be a risk factor for SIP, because it was used in only one infant with SIP in this study. Other risk factors reported in previous studies associated with SIP, such as exposure to inotropic agents and surfactants [28], were not significant. Immature gastrointestinal motility and thickening of the meconium would exert mechanical compression on the bowel wall, making the patient susceptible to mucosa damage, ischemia, and perforation [6,13]. In addition, various infections, especially those caused by Candida species, have been reported to be related to SIP [6]. In this study, one case of Enterococcus and one case of GBS were detected in the blood cultures of infants in the SIP group. However, the relationship between sepsis and the occurrence of SIP in ELBWIs with gasless abdomen could not be evaluated in this study because of the small number of cases. Further research in this aspect is warranted.
In general, infants with SIP have no typical symptoms or signs of NEC, such as abdominal distension, abdominal rigidity, tenderness, abdominal wall edema, or erythema [29]. These infants do not meet the traditionally accepted BellŌĆÖs criteria for NEC [6]. They are often strikingly stable in the early stage and have no signs of severe illness or peritonitis [5,15]. Their abdominal radiography commonly shows gasless abdomen [6]. Hence, perforation may be difficult to diagnose, particularly in ELBWIs with gasless abdomen, which may delay prompt and adequate surgical intervention [1,2,4,5,29]. Gray or bluish discoloration of the abdominal wall, resulting from peritoneal staining by spillage of meconium into the peritoneal cavity, that it should be regarded as a typical sign of perforation, and this discoloration usually starts in the groin or scrotum [5,16]. In this study, these findings were observed in six of the infants (75%) with SIP, and non-specific findings such as greenish or red gastric residues, abdominal distension, and decreased bowel sounds, were common in infants with SIP.
Previous studies have reported that abdominal ultrasonography may be a very useful tool for diagnosis of SIP [1,2]. In particular, the presence of extraluminal free-floating hyperechogenic materials could suggest the occurrence of intestinal perforation in ELBWIs with gasless or scanty gas abdomen [1]. Extraluminal echogenic materials and intraluminal echogenicity were observed in four (50%) and six infants (75%) with SIP, respectively, in this study. However, these findings should not be interpreted as definite signs of intestinal perforation, because their specificity was reported to be only 89.0% [1]. All infants with the above-mentioned abdominal ultrasonographic findings were operated on, and the presence of SIP was confirmed.
Treatment options for SIP in ELBWIs are primary laparotomy with resection or primary peritoneal drainage [19,30-33]. Although previous studies did not reveal a clear difference in prognosis between infants who underwent peritoneal drainage and those who underwent primary surgical repair [32], there is compelling evidence that infants who underwent peritoneal drainage show inferior neurologic outcomes at 18 to 22 months of age [33]. In this study, three patients underwent peritoneal drainage followed by salvage laparotomy. These three infants had unstable vital signs at the first intervention, and peritoneal drainage was preferred over primary laparotomy with resection of perforated segments. Primary laparotomy was performed in the other five infants. However, despite the surgical treatment and subsequent intensive care, four infants (50.0%) died after operation. It was presumed that three of them died owing to postoperative bleeding resulting from disseminated intravascular coagulation occurring during the surgery. Therefore, early diagnosis and surgery are required.
This study has several limitations. First, this study was conducted retrospectively in a single center, and included only a small number of ELBWIs with persistent gasless abdomen on abdominal radiography. Thus, the exact incidence and prognosis of SIP in ELBWIs with gasless abdomen could not be predicted. Second, because the clinical and radiologic findings suggestive of SIP in ELBWIs in this study would be non-specific and might present in other gastrointestinal disorders, such as NEC, the results indicating that these clinical findings may be associated with intestinal perforation in ELBWIs with gasless abdomen should be interpreted with caution. However, despite the above limitations, the findings of abdominal ultrasonography in this study such as extraluminal echogenic materials and intraluminal echogenicity may be helpful for early detection of a slowly progressive intestinal perforation in ELBWIs with gasless abdomen.
In conclusion, this study showed that SIP could commonly occur in ELBWIs who show persistent gasless abdomen on simple abdominal radiography, and gray or bluish discoloration of the abdomen suggestive of meconium peritonitis was frequently observed in infants with SIP. Moreover, this study showed that abdominal ultrasound could be a highly useful for the diagnosis of SIP.
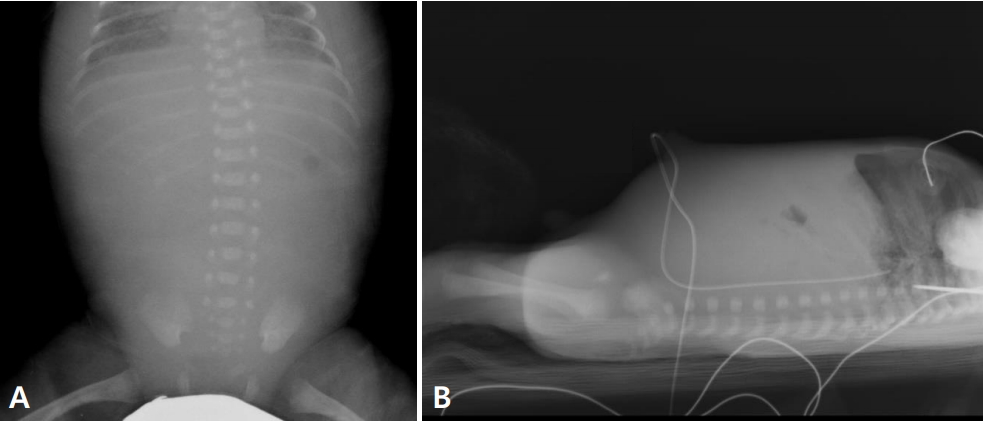
Figure┬Ā1.
Gasless abdomen on simple abdominal radiography supine (A) and cross-table lateral (B) views show gasless or scanty gas abdomen.
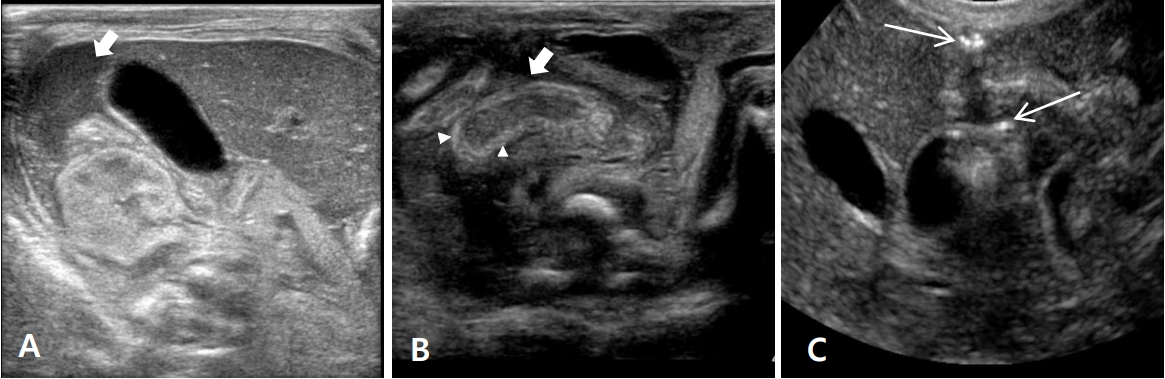
Figure┬Ā2.
Abdominal ultrasonographic findings suggestive of intestinal perforation in extremely low-birthweight infants with gasless abdomen on simple abdominal radiography. (A) Fluid collection with heterogenous echogenecities is observed in the extraluminal space (short arrow). (B) Bowel wall thickening (short arrow) and increased intramural echogenicity (arrowheads) are observed. (C) Two tiny echogenic air bubbles are observed in the extraluminal space (long arrows).
Table┬Ā1.
Perinatal and Neonatal Characteristics of Enrolled Infants
Values are expressed as mean┬▒standard deviation or number (%).
Abbreviations: SIP, spontaneous intestinal perforation; PROM, premature rupture of membrane; SGA, small for gestational age, RDS, respiratory distress syndrome; PDA, patent ductus arteriosus; IV, intravenous; BPD bronchopulmonary dysplasia; IVH, intraventricular hemorrhage; ROP, retinopathy of prematurity.
Table┬Ā2.
Perioperative Feeding History and Clinical Findings Suggestive of Intestinal Perforation
Table┬Ā3.
Radiologic Findings Suggestive of Spontaneous Intestinal Perforation
Table┬Ā4.
Operative Findings and Postoperative Outcomes
REFERENCES
1. Fischer A, Vachon L, Durand M, Cayabyab RG. Ultrasound to diagnose spontaneous intestinal perforation in infants weighing Ōēż 1000 g at birth. J Perinatol 2015;35:104ŌĆō9.



2. Miller SF, Seibert JJ, Kinder DL, Wilson AR. Use of ultrasound in the detection of occult bowel perforation in neonates. J Ultrasound Med 1993;12:531ŌĆō5.


3. Attridge JT, Herman AC, Gurka MJ, Griffin MP, McGahren ED, Gordon PV. Discharge outcomes of extremely low birth weight infants with spontaneous intestinal perforations. J Perinatol 2006;26:49ŌĆō54.



4. Pumberger W, Mayr M, Kohlhauser C, Weninger M. Spontaneous localized intestinal perforation in very-low-birth-weight infants: a distinct clinical entity different from necrotizing enterocolitis. J Am Coll Surg 2002;195:796ŌĆō803.



5. Mintz AC, Applebaum H. Focal gastrointestinal perforations not associated with necrotizing enterocolitis in very low birth weight neonates. J Pediatr Surg 1993;28:857ŌĆō60.


6. Adderson EE, Pappin A, Pavia AT. Spontaneous intestinal perforation in premature infants: a distinct clinical entity associated with systemic candidiasis. J Pediatr Surg 1998;33:1463ŌĆō7.


7. Seibert JJ, Williamson SL, Golladay ES, Mollitt DL, Seibert RW, Sutterfield SL. The distended gasless abdomen: a fertile field for ultrasound. J Ultrasound Med 1986;5:301ŌĆō8.


8. Oretti C, Bussani R, Janes A, Demarini S. Multiple segmental absence of intestinal musculature presenting as spontaneous isolated perforation in an extremely low-birth-weight infant. J Pediatr Surg 2010;45:E25ŌĆō7.

9. Kubota A, Yamanaka H, Okuyama H, Shiraishi J, Kawahara H, Hasegawa T, et al. Focal intestinal perforation in extremelylow-birth-weight neonates: etiological consideration from histological findings. Pediatr Surg Int 2007;23:997ŌĆō1000.



10. Dzieniecka M, Grzelak-Krzymianowska A, Kulig A. Segmental congenital defect of the intestinal musculature. Pol J Pathol 2010;61:94ŌĆō6.

11. Kang J, Im IJ, Lee DS, Go JH, Chang YP. A case of spontaneous focal Intestinal perforation due to defect of the intestinal musculature. J Korean Soc Neonatol 2006;13:180ŌĆō3.
12. Buyuktiryaki M, Kanmaz HG, Okur N, Ates U, Sirvan AL, Uras N. Segmental absence of intestinal muscle with ileal web in an extremely low birth weight infant: case report. Arch Argent Pediatr 2016;114:e108ŌĆō10.

13. Gordon PV. Understanding intestinal vulnerability to perforation in the extremely low birth weight infant. Pediatr Res 2009;65:138ŌĆō44.


14. Tatekawa Y, Muraji T, Imai Y, Nishijima E, Tsugawa C. The mechanism of focal intestinal perforations in neonates with low birth weight. Pediatr Surg Int 1999;15:549ŌĆō52.



15. Meyer CL, Payne NR, Roback SA. Spontaneous, isolated intestinal perforations in neonates with birth weight less than 1,000 g not associated with necrotizing enterocolitis. J Pediatr Surg 1991;26:714ŌĆō7.


16. Choi SY, Choi IJ, Kim SM, Jung JH, Kim GH, Son CM. Spontaneous ileal perforation in very low birth weight infant without evidence of necrotizing enterocolitis. J Korean Soc Neonatol 2004;11:77ŌĆō80.
17. Shah TA, Meinzen-Derr J, Gratton T, Steichen J, Donovan EF, Yolton K, et al. Hospital and neurodevelopmental outcomes of extremely low-birth-weight infants with necrotizing enterocolitis and spontaneous intestinal perforation. J Perinatol 2012;32:552ŌĆō8.



18. Gordon PV, Attridge JT. Understanding clinical literature relevant to spontaneous intestinal perforations. Am J Perinatol 2009;26:309ŌĆō16.


19. Jakaitis BM, Bhatia AM. Definitive peritoneal drainage in the extremely low birth weight infant with spontaneous intestinal perforation: predictors and hospital outcomes. J Perinatol 2015;35:607ŌĆō11.



20. Tiwari C, Sandlas G, Jayaswal S, Shah H. Spontaneous intestinal perforation in neonates. J Neonatal Surg 2015;4:14.




21. Holland AJ, Shun A, Martin HC, Cooke-Yarborough C, Holland J. Small bowel perforation in the premature neonate: congenital or acquired? Pediatr Surg Int 2003;19:489ŌĆō94.



22. Attridge JT, Clark R, Walker MW, Gordon PV. New insights into spontaneous intestinal perforation using a national data set: (2) two populations of patients with perforations. J Perinatol 2006;26:185ŌĆō8.



23. Gordon PV, Young ML, Marshall DD. Focal small bowel perforation: an adverse effect of early postnatal dexamethasone therapy in extremely low birth weight infants. J Perinatol 2001;21:156ŌĆō60.



24. Paquette L, Friedlich P, Ramanathan R, Seri I. Concurrent use of indomethacin and dexamethasone increases the risk of spontaneous intestinal perforation in very low birth weight neonates. J Perinatol 2006;26:486ŌĆō92.




25. Attridge JT, Clark R, Gordon PV. New insights into spontaneous intestinal perforation using a national data set (3): antenatal steroids have no adverse association with spontaneous intestinal perforation. J Perinatol 2006;26:667ŌĆō70.



26. Attridge JT, Clark R, Walker MW, Gordon PV. New insights into spontaneous intestinal perforation using a national data set: (1) SIP is associated with early indomethacin exposure. J Perinatol 2006;26:93ŌĆō9.




27. Tatli MM, Kumral A, Duman N, Demir K, Gurcu O, Ozkan H. Spontaneous intestinal perforation after oral ibuprofen treatment of patent ductus arteriosus in two very-low-birthweight infants. Acta Paediatr 2004;93:999ŌĆō1001.


28. Shah J, Singhal N, da Silva O, Rouvinez-Bouali N, Seshia M, Lee SK, et al. Intestinal perforation in very preterm neonates: risk factors and outcomes. J Perinatol 2015;35:595ŌĆō600.



29. Buchheit JQ, Stewart DL. Clinical comparison of localized intestinal perforation and necrotizing enterocolitis in neonates. Pediatrics 1994;93:32ŌĆō6.



30. Blakely ML, Lally KP, McDonald S, Brown RL, Barnhart DC, Ricketts RR, et al. Postoperative outcomes of extremely low birth-weight infants with necrotizing enterocolitis or isolated intestinal perforation: a prospective cohort study by the NICHD Neonatal Research Network. Ann Surg 2005;241:984ŌĆō9.



31. Gebus M, Michel JL, Samperiz S, Harper L, Alessandri JL, Ramful D. Management of neonatal spontaneous intestinal perforation by peritoneal needle aspiration. J Perinatol 2018;38:159ŌĆō63.



-
METRICS

-
- 1 Crossref
- 11,289 View
- 169 Download
- Related articles in NM
-
Risk Factors for Rickets of Prematurity in Extremely Low Birth Weight Infants.2015 November;22(4)






