 |
 |
- Search
| Neonatal Med > Volume 25(3); 2018 > Article |
|
Abstract
Purpose
Congenital diaphragmatic hernia (CDH) is rare but potentially fatal. The overall outcome is highly variable. This study aimed to identify a simple and dynamic parameter that helps predict the mortality of CDH patients in real time, without invasive tests.
Methods
We conducted a retrospective chart review of 59 CDH cases. Maternal and fetal information included the gestational age at diagnosis, site of defect, presence of liver herniation, and lung-to-head ratio (LHR) at 20 to 29 weeks of gestational age. Information regarding postnatal treatment, including the number of days until surgery, the need for inhaled nitric oxide (iNO), the need for extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO), and survival, was collected. The highest respiratory severity score (RSS) within 24 hours after birth was also calculated.
Results
Statistical analysis showed that a younger gestational age at the initial diagnosis (P<0.001), a lower LHR (P=0.001), and the presence of liver herniation (P= 0.003) were prenatal risk factors for CDH mortality. The RSS and use of iNO and ECMO were significant factors affecting survival. In the multivariate analysis, the only remaining significant risk factor was the highest preoperative RSS within 24 hours after birth (P=0.002). The area under the receiver operating characteristic curve was 0.9375, with a sensitivity of 91.67% and specificity of 83.87% at the RSS cut-off value of 5.2. The positive and negative predictive values were 82.14% and 92.86%, respectively.
Congenital diaphragmatic hernia (CDH) is rare but potentially fatal and affects neonates in one out of every 3,000 live births [1]. The severity of pulmonary hypertension due to pulmonary hypoplasia is the major factor in mortality and morbidity. Because the overall outcome is highly variable, the management plan is not uniform [2]. There have been many efforts to predict the postnatal outcomes of CDH so that risk stratification can direct the planning of tailored management [2-6]. However, these predictive models are difficult to apply, too complex to understand intuitively, and are not able to reflect postnatal progress in real time. Our study begins with the design of a simple and dynamic parameter that reflects the postnatal changes of CDH patients in real time, without a blood test or echocardiogram.
The purpose of the present study was to identify risk factors for predicting the mortality of CDH neonates. We aimed to address this goal with the respiratory severity score (RSS), which is the product of the mean airway pressure (MAP) and the fraction of inspired oxygen (FiO2). The RSS was first described in 2004 as an index for the non-invasive assessment of ventilatory status [7]. The RSS has been used in clinical trials as a modified surrogate of the oxygenation index (OI; FiO2×MAP×100/partial pressure of oxygen in arterial blood [PaO2]) [7-10], and a strong association between the RSS and OI in ventilated newborns was demonstrated in one study [11].
Seoul National University Children’s Hospital (SNUCH) is a tertiary hospital in Seoul, Korea. We have 40 beds in the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU), and approximately 600 neonates are admitted every year. Support from pediatric professionals, including subspecialists and surgeons, is well available for medical intervention or surgery. SNUCH is a high-volume case center (annual repair case number >6), as per a study that reported the effect of hospital case volume on the outcome of CDH [12].
We conducted a retrospective chart review of CDH cases admitted between December 2006 and June 2015. All live inborn and outborn CDH infants admitted to the NICU of SNUCH within 24 hours after birth were included.
The acute postnatal management protocol was as follows. All newborns diagnosed with CDH prenatally were delivered with attending pediatric doctors. Immediate intubation was performed after birth, and mechanical ventilator support was initiated using either conventional or high-frequency oscillatory ventilation mode at the NICU. The target range of oxygen saturation was 85% to 95% by pulse oximetry [13]. We clinically assessed the possibility of pulmonary hypertension in patients with a pre- and post-ductal peripheral oxygen saturation (SpO2) difference of ≥10%. Echocardiograms were performed before and after surgery to assess the degree of pulmonary hypertension. The diagnostic criteria for pulmonary hypertension were: (1) tricuspid valve regurgitation (TR) velocity ≥3 m/sec in the absence of pulmonary stenosis, (2) flat or left-deviated interventricular septal shape, and (3) right-to-left shunt or rightto-left dominant bidirectional shunt flow through the patent ductus arteriosus [14]. Patients were classified into three groups according to estimated pulmonary arterial pressure relative to systemic systolic blood pressure: less than 2/3 of systemic systolic pressure (no/mild pulmonary hypertension), equal to or greater than 2/3 of systemic-to-systemic pressure (moderate pulmonary hypertension), or systemic-to-suprasystemic pressure (severe pulmonary hypertension). The assessment hierarchy was: (1) pressure differential by direction and velocity of ductus arteriosus flow using the Bernoulli equation; (2) 2-dimensional interventricular septum position (parasternal short axis), graded as normal, flattened (indicating right ventricular pressure ≥2/3 systemic pressure), or D-shaped (right ventricular pressure considered to be systemic-to-suprasystemic pressure); and (3) right ventricular pressures based on peak TR jet velocity estimated by the modified Bernoulli equation (assuming a right atrial pressure of 0 mm Hg ) [15,16].
We provided inhaled nitric oxide (iNO) therapy to infants with pulmonary hypertension if they showed evidence of extrapulmonary right-to-left shunting and if the OI was greater than 25 after effective lung recruitment [13,17]. The usual starting dose was 20 ppm. Additionally, hemodynamic support comprising volume expansion or the administration of catecholamines was conducted when necessary. We performed extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) procedure if a patient with pulmonary hypertension did not respond to medical therapy or if the OI was elevated above 40 [18-20], except when the patient was less than 34 weeks of gestational age or weighed less than 2 kg. Other indications for ECMO included increased PaCO2 and refractory respiratory acidosis with pH <7.15. Usually we preferred immediate (<24 hours after birth) repair after initial stabilization with a gentle ventilation technique rather than delayed (>48 hours after birth) repair of CDH because no known definitive benefit of prolonged stabilization of CDH patients before repair surgery has been demonstrated to date [21,22]. Repair surgery was performed in patients on ECMO in some cases.
The variables collected for analysis included gestational age, birth weight, sex, and other combined anomalies. The collected information regarding postnatal treatment included the number of days until surgery, the need for iNO, the need for ECMO, and survival. The RSS (MAP×FiO2) was calculated hourly during the 24 hours after birth. If the conventional ventilator mode was used, the MAP was calculated as MAP=PEEP+[(PIP–PEEP)×(ti/ti+te)] (PEEP, positive end-expiratory pressure; PIP, peak inspiratory pressure; ti, the inspiratory time; te, the expiratory time) [23]. If the high frequency oscillatory ventilator mode was applied, the MAP of the actual ventilator setting was used for calculating RSS. Additionally, maternal information was collected. Data included demographics, antenatal history, mode of delivery, and fetal information, including the gestational age at CDH diagnosis, the site of defect, the presence of liver herniation, and the lung-to-head ratio (LHR), only if the measurement was taken from a sonogram that had been performed at 20 to 29 weeks of gestational age.
Demographic data and predictors of outcome that were found and published previously were examined by univariate analyses with independent t-tests and Wilcoxon rank-sum tests. The chi-square test was used to evaluate categorical data, and the Mann-Whitney U-test was used for all continuous variable comparisons. P<0.05 was considered statistically significant. Factors thought to be useful for the pretreatment stratification scheme were examined with multivariate logistic regression analysis. Cox proportional hazards multivariate models were generated to assess the relationship between the risk factors of CDH and mortality. Area under the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve (AUC) analysis was used to determine the cut-off value of the predictive factor. Data were described as the mean±standard deviation and the range or as the rate. All statistical analyses were performed using SPSS version 24.0 (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA) and STATA version 12.1 (STATA Corp., College Station, TX, USA).
A total of 59 infants who were diagnosed with CDH and admitted to the NICU during the study period were included in the analysis. A flow chart of the disease course is presented in Figure 1. Preoperative ECMO was performed in five patients, and among them, one patient also underwent postoperative ECMO. One patient who underwent ECMO but not surgery expired. All 13 patients without surgical intervention died, regardless of whether ECMO was performed. Diaphragmatic hernia repair was performed in 46 neonates, and the number of survivors was 34.
The baseline characteristics of the patients are shown in Table 1. The mean gestational age was 38.71±1.43 weeks, and the mean birthweight was 3,001±510 g.
First, we analyzed the presumptive prenatal risk factors for CDH mortality. The results of statistical analysis indicated that a younger gestational age at initial diagnosis (P<0.001), a lower LHR (P=0.001), and the presence of liver herniation (P=0.003) were significantly associated with CDH mortality in the study. The differences in these factors between the survival and the death groups are presented in Table 2.
Possible postnatal risk factors for CDH, including hernia repair surgery, the number of days from birth to the day of surgery, the highest preoperative and postoperative RSSs within 24 hours after birth, the application of preoperative and postoperative iNO, and the application of preoperative and postoperative ECMO, are compared in Table 3. All survivors had repair operations. Additionally, the RSS, application of iNO and ECMO were statistically significant factors that affected the survival rate.
Multivariate analysis was performed using the aforementioned statistically significant factors. The only remaining significant factor affecting CDH mortality was the highest preoperative RSS within 24 hours after birth (P=0.002) (Table 4).
ROC analysis of the preoperative RSS was performed to identify the appropriate cut-off value predictive of mortality (Figure 2). The AUC was 0.9375, with a sensitivity of 91.67% and a specificity of 83.87% at a cut-off value of 5.2. The positive and negative predictive values were 82.14% and 92.86%, respectively.
To our knowledge, the present study is the first evaluation of the relationship between RSS and CDH. We found that the preoperative RSS within 24 hours after birth was the most significant predictive factor; the cut-off value had acceptable sensitivity and specificity according to ROC curve analysis for the prognoses of CDH neonates. The positive and negative predictive values were also reasonable. The contribution of this study involves the finding and suggesting of a possible postnatal respiratory predictive factor for the prognosis of CDH.
Originally, RSS was designed under conditions in which PaO2 measurements were not routinely performed because not all patients had umbilical arterial catheters. Indwelling arterial catheters are required for the frequent monitoring of other respiratory indices, such as OI, and thus, complications including thrombosis and infection are potential burdens [24,25]. Furthermore, the risk of iatrogenic anemia following blood samplings that often requiring multiple blood transfusions should be a concern [26]. However, when using the RSS, there is no need to perform frequent blood sampling, and hence, the effort and risk are reduced. Previous studies suggested that using the RSS as a respiratory index can be an option for less invasive intensive care, especially for the most vulnerable patients in the NICU. One study reported that the RSS on day 30 of life can provide useful prognostic information for very low birth weight infants undergoing prolonged mechanical ventilation [9]. Recently, a study addressing RSS and extubation readiness in very low birth weight infants was published [27]. These reports, along with ours, suggest that the RSS can be used as a reliable respiratory predictive factor.
To date, several studies have addressed the factors which can predict the prognoses of CDH neonates, but no standardized, universally accepted method has been identified. Known candidate prenatal evaluation factors, such as the gestational age when the initial diagnosis was made, the LHR, and liver herniation, have been proposed, but they are insufficient to reflect variable changes in the postnatal disease course because they are fixed values at a single moment during the prenatal period. Additionally, another problem exists wherein a measured value, such as the LHR, is originally subjective and operator dependent. Recently, the Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia Study Group suggested a scoring equation with multiple variables, such as birth weight, Apgar scores, the presence of severe pulmonary hypertension at the first echocardiogram, a major cardiac anomaly, and chromosomal anomaly [2]. However, these are all fixed factors at a single evaluation, and hence, cannot reflect the dynamic disease course of this group of patients. Conversely, the RSS is the product of 2 real-time values and is thus able to promptly reflect the changing conditions of patients. The values can be objectively measured and easily obtained without any invasive procedure. This is the specific usefulness of the RSS as a dynamic prognostic predictive factor and the very strength of the present study.
All neonates who died before surgery had conditions that were not favorable to repair operations. Our results showed significant differences between the survivor and non-survivor groups regarding the application of iNO and ECMO. iNO improves oxygenation, and reduces the need for ECMO in neonates with persistent pulmonary hypertension [28]. However, no randomized trial has demonstrated that iNO improves the outcomes of CDH patients. Moreover, two well-designed trials found that early iNO treatment fails to improve survival or reduce the need for ECMO in newborns with CDH [29]. Even the possibility of increasing the need for ECMO in CDH patients treated with iNO has been suggested [30]. The poorer outcome in our patients who were treated with iNO could be partially explained by these findings [31]. The benefit of ECMO for CDH patients is still unclear [18]. The benefit of delayed surgery after ECMO rather than emergency surgery on ECMO was reported previously, but there has been no convincing reduction in mortality with ECMO in randomized trials. In our study, all patients who received the ECMO either pre- or post- operatively died. As noted, we consider ECMO use mainly if the OI exceeds 40. However, because of the invasiveness of the procedure and known poor long-term outcome [32], we tend to avoid ECMO use as long as the neonate can withstand the disease course. As a result, the most seriously ill patient who did not respond to other treatments would have been chosen to receive ECMO. Thus, we think that some degree of selection bias affected the higher mortality of the ECMO group. This tendency in treatment strategies is observed in another study in Japan [33].
The present study may have several limitations because it is based on a retrospective chart review in a single center. Additionally, during the study period, there were quantitative and qualitative changes in the NICU. Therefore, gradual changes in clinical practice over 10 years, such as in the ventilation strategy, treatment of pulmonary hypertension, and timing of surgery may not have been adequately corrected for in the results. A prospective multicenter study with a precisely designed protocol will be needed to address this issue. Furthermore, the high mortality and morbidity of the CDH patient group arise from refractory pulmonary hypertension. Thus, the medical approach to these patients is mainly focused on treating pulmonary hypertension, which is unavoidably accompanied by pulmonary hypoplasia. Future studies should consider using the RSS to evaluate the efficacies of new therapies, including medicine and ventilator modalities, for refractory pulmonary hypertension in CDH patients.
In conclusion, we confirmed that the highest RSS value measured within 24 hours after birth is related to the prognosis of CDH. The RSS is an index that can be calculated in real-time from the ventilator setting without invasive testing. Therefore, using the RSS as a prognostic predictor with simple calculations may help clinicians plan to manage CDH patients.
Figure 1.
Flow chart of disease course in patients admitted between December 2006 and June 2015. Abbreviations: CDH, congenital diaphragmatic hernia; ECMO, extracorporeal membrane oxygenation.
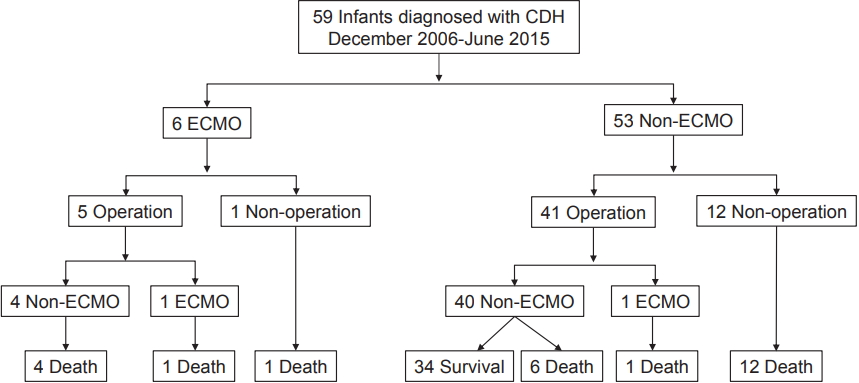
Figure 2.
Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve of the highest pre-operative respiratory severity score within 24 hours after birth.
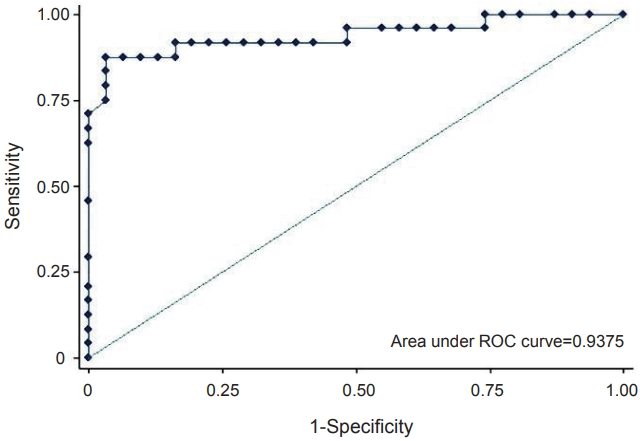
Table 1.
Baseline Characteristics of Study Object Infants with Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia (n=59)
Table 2.
Prenatal Risk Factors for the Mortality of Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia
Table 3.
Postnatal Risk Factors for the Mortality of Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia
Table 4.
Risk Factors for the Mortality of Congenital Diaphrag-matic Hernia by Multivariate Analysis
REFERENCES
1. Barriere F, Michel F, Loundou AD, Fouquet V, Kermorvant E, Blanc S, et al. One-year outcome for congenital diaphragmatic hernia: results from the French National Register. J Pediatr 2018;193:204–10.


2. Brindle ME, Cook EF, Tibboel D, Lally PA, Lally KP, Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia Study Group. A clinical prediction rule for the severity of congenital diaphragmatic hernias in newborns. Pediatrics 2014;134:e413–9.


3. Schultz CM, DiGeronimo RJ, Yoder BA, Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia Study Group. Congenital diaphragmatic hernia: a simplified postnatal predictor of outcome. J Pediatr Surg 2007;42:510–6.


4. van den Hout L, Reiss I, Felix JF, Hop WC, Lally PA, Lally KP, et al. Risk factors for chronic lung disease and mortality in newborns with congenital diaphragmatic hernia. Neonatology 2010;98:370–80.


5. Akinkuotu AC, Cruz SM, Abbas PI, Lee TC, Welty SE, Olutoye OO, et al. Risk-stratification of severity for infants with CDH: prenatal versus postnatal predictors of outcome. J Pediatr Surg 2016;51:44–8.


6. Baird R, MacNab YC, Skarsgard ED, Canadian Pediatric Surgery Network. Mortality prediction in congenital diaphragmatic hernia. J Pediatr Surg 2008;43:783–7.


7. Merrill JD, Ballard RA, Cnaan A, Hibbs AM, Godinez RI, Godinez MH, et al. Dysfunction of pulmonary surfactant in chronically ventilated premature infants. Pediatr Res 2004;56:918–26.


8. Katz LA, Klein JM. Repeat surfactant therapy for postsurfactant slump. J Perinatol 2006;26:414–22.



9. Malkar MB, Gardner WP, Mandy GT, Stenger MR, Nelin LD, Shepherd EG, et al. Respiratory severity score on day of life 30 is predictive of mortality and the length of mechanical ventilation in premature infants with protracted ventilation. Pediatr Pulmonol 2015;50:363–9.


10. Ballard RA, Truog WE, Cnaan A, Martin RJ, Ballard PL, Merrill JD, et al. Inhaled nitric oxide in preterm infants undergoing mechanical ventilation. N Engl J Med 2006;355:343–53.


11. Iyer NP, Mhanna MJ. Non-invasively derived respiratory severity score and oxygenation index in ventilated newborn infants. Pediatr Pulmonol 2013;48:364–9.


12. Grushka JR, Laberge JM, Puligandla P, Skarsgard ED, Canadian Pediatric Surgery Network. Effect of hospital case volume on outcome in congenital diaphragmatic hernia: the experience of the Canadian Pediatric Surgery Network. J Pediatr Surg 2009;44:873–6.


13. Weems MF, Jancelewicz T, Sandhu HS. Congenital diaphragmatic hernia: maximizing survival. NeoReviews 2016;17:e705. –18.

14. Kim SY, Shin SH, Kim HS, Jung YH, Kim EK, Choi JH. Pulmonary arterial hypertension after ibuprofen treatment for patent ductus arteriosus in very low birth weight infants. J Pediatr 2016;179:49. –53. e1.


15. Lusk LA, Wai KC, Moon-Grady AJ, Steurer MA, Keller RL. Persistence of pulmonary hypertension by echocardiography predicts short-term outcomes in congenital diaphragmatic hernia. J Pediatr 2015;166:251. –6. e1.


16. Keller RL, Tacy TA, Hendricks-Munoz K, Xu J, Moon-Grady AJ, Neuhaus J, et al. Congenital diaphragmatic hernia: endothelin-1, pulmonary hypertension, and disease severity. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2010;182:555–61.



17. Abman SH, Hansmann G, Archer SL, Ivy DD, Adatia I, Chung WK, et al. Pediatric pulmonary hypertension: guidelines from the American Heart Association and American Thoracic Society. Circulation 2015;132:2037–99.


18. Snoek KG, Reiss IK, Greenough A, Capolupo I, Urlesberger B, Wessel L, et al. Standardized postnatal management of infants with congenital diaphragmatic hernia in Europe: The CDH EURO Consortium Consensus 2015 Update. Neonatology 2016;110:66–74.


19. McHoney M, Hammond P. Role of ECMO in congenital diaphragmatic hernia. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed 2018;103:F178–81.


20. Fletcher K, Chapman R, Keene S. An overview of medical ECMO for neonates. Semin Perinatol 2018;42:68–79.


21. Hollinger LE, Lally PA, Tsao K, Wray CJ, Lally KP, Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia Study Group. A risk-stratified analysis of delayed congenital diaphragmatic hernia repair: does timing of operation matter? Surgery 2014;156:475–82.


22. Kamata S, Usui N, Ishikawa S, Okuyama H, Kitayama Y, Sawai T, et al. Prolonged preoperative stabilization using high-frequency oscillatory ventilation does not improve the outcome in neonates with congenital diaphragmatic hernia. Pediatr Surg Int 1998;13:542–6.


23. Glenski JA, Marsh HM, Hall RT. Calculation of mean airway pressure during mechanical ventilation in neonates. Crit Care Med 1984;12:642–4.


24. Green C, Yohannan MD. Umbilical arterial and venous catheters: placement, use, and complications. Neonatal Netw 1998;17:23–8.
25. Huning BM, Horsch S, Roll C. Blood sampling via umbilical vein catheters decreases cerebral oxygenation and blood volume in preterm infants. Acta Paediatr 2007;96:1617–21.


26. Del Vecchio A, Franco C, Petrillo F, D'Amato G. Neonatal transfusion practice: when do neonates need red blood cells or platelets? Am J Perinatol 2016;33:1079–84.



27. Mhanna MJ, Iyer NP, Piraino S, Jain M. Respiratory severity score and extubation readiness in very low birth weight infants. Pediatr Neonatol 2017;58:523–8.


28. DiBlasi RM, Myers TR, Hess DR. Evidence-based clinical practice guideline: inhaled nitric oxide for neonates with acute hypoxic respiratory failure. Respir Care 2010;55:1717–45.

29. Campbell BT, Herbst KW, Briden KE, Neff S, Ruscher KA, Hagadorn JI. Inhaled nitric oxide use in neonates with congenital diaphragmatic hernia. Pediatrics 2014;134:e420. –6.


30. The Neonatal Inhaled Nitric Oxide Study Group (NINOS). Inhaled nitric oxide and hypoxic respiratory failure in infants with congenital diaphragmatic hernia. Pediatrics 1997;99:838–45.


31. Putnam LR, Tsao K, Morini F, Lally PA, Miller CC, Lally KP, et al. Evaluation of variability in inhaled nitric oxide use and pulmonary hypertension in patients with congenital diaphragmatic hernia. JAMA Pediatr 2016;170:1188–94.


-
METRICS

-
- 5 Crossref
- 8,212 View
- 166 Download
- Related articles in NM
-
Four Cases of Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation for Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia.2009 May;16(1)





