 |
 |
- Search
| Neonatal Med > Volume 28(2); 2021 > Article |
|
Abstract
Purpose
We investigated whether consecutive levels of new emerging renal biomarkers, including serum cystatin C (CysC) and urinary neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL)/creatinine (Cr) ratio, were affected by postconceptional age in very-low-birth-weight (VLBW) infants.
Methods
Repeatedly measured samples for each infant were divided into four groups according to postnatal age: at birth (stage I), 3 to 7 days postnatally (stage II), 8 to 28 days postnatally (stage III), and >28 days postnatally (stage IV). The association between renal biomarkers and postconceptional age was assessed using Pearson’s correlation coefficient, and the mean values of renal biomarkers in the four stages were compared using repeated-measures analysis of variance.
Results
For samples measured at birth, serum CysC (r=–0.358, P=0.032) and urinary NGAL/Cr ratio (r=–0.522, P=0.001) were negatively correlated with gestational age, whereas serum Cr (r=0.148, P=0.390) was not. In addition, for all samples measured, serum CysC (r=–0.209, P=0.012), urinary NGAL/Cr ratio (r=–0.536, P<0.001), and serum Cr (r=–0.311, P<0.001) were negatively correlated with postconceptional age. Compared with the mean values of the postnatal age-specific stages, serum CysC showed no significant differences in any of the four stages. However, the urinary NGAL/Cr ratio in stage IV was significantly different from those in stages I to III.
Conclusion
Although urinary NGAL/Cr ratio and serum CysC were negatively correlated with postconceptional age considering renal development, serum CysC showed no significant differences in any of the four postnatal age-specific stages. Urinary NGAL/Cr ratio at >28 days postnatally seems to be more affected by postconceptional age than serum CysC in VLBW infants.
Despite recent improvements in the survival rates of very-low-birth-weight (VLBW) infants (birth weight [BW] <1,500 g), kidney dysfunction remains associated with poor outcomes [1,2] . Because nephron development is completed between 32 and 36 weeks of gestation [3], VLBW infants have small nephrons due to their lower gestational ages [4]. Renal function depends on nephron mass, which is proportional to the number of perfused glomeruli [5]. Accordingly, VLBW infants are at a high risk of impaired renal function and are more vulnerable to renal injury caused by antibiotics and nephrotoxic medications [6-8]. However, unlike respiratory and cerebral functions, renal function in VLBW infants has not been thoroughly studied. Glomerular filtration rate (GFR) is the best measure of renal function [9]. However, accurate measurement of GFR in VLBW infants is problematic owing to a lack of availability of the gold standard inulin.
Serum creatinine (Cr) is traditionally used to estimate GFR. Despite its wide application, its use is associated with several limitations. In particular, Cr levels may not change until 25% to 50% of kidney function has already been lost, and renal function may be overestimated at low GFR [10]. Additionally, serum Cr concentration can be affected by maternal Cr levels for the first few days after birth [11-13], and depends on gestational age and postnatal age in preterm infants [13,14]. Therefore, consecutive changes in serum Cr levels after birth may make it difficult to monitor renal function in VLBW infants.
Cystatin C (CysC) is a low-molecular-weight protein that is eliminated exclusively through glomerular filtration and metabolized in proximal renal tubular cells [15]. Therefore, serum CysC reflects GFR, whereas urinary CysC indicates renal tubular dysfunction [15]. Notably, CysC is not affected by BW or gestational age in preterm infants [16,17] and cannot be transferred across the placental barrier [18]. According to a meta-analysis, serum CysC shows better diagnostic sensitivity than serum Cr [19].
Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) may also be a sensitive promising biomarker for renal injury [20]. After nephrotoxic and ischemic injury, NGAL accumulates at high levels in the cortical tubules and urine [21]. NGAL can also be detected in the urine of VLBW infants with ongoing nephrogenesis [22]. In a cohort study, urinary NGAL was found to be a useful marker for predicting the elevation of serum Cr [23]. However, urinary NGAL levels could be confounded by hydration state and urine output [24].
Previously, we revealed that the urinary NGAL/Cr ratio was negatively correlated with postnatal age in VLBW infants, but serum CysC did not [25]. However, renal development based on gestational age at birth was not considered while comparing renal biomarkers with postnatal age. Therefore, in this study, we focused on the changes in these biomarkers and their associations with postconceptional age in VLBW infants.
We retrospectively reviewed the medical records of surviving VLBW infants admitted to the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) of the Keimyung University Dongsan Medical Center, Daegu, South Korea, between May 2015 and April 2017. For each infant whose renal biomarkers, including serum CysC, urinary NGAL/Cr ratio, and serum Cr, were consecutively measured during hospitalization, we recorded the age at which the samples were measured and then divided the renal biomarkers into four groups according to postnatal age: at birth (stage I), 3 to 7 days postnatally (stage II), 8 to 28 days postnatally (stage III), and greater than 28 days postnatally (stage IV). We excluded infants with Apgar scores of less than 5 at 5 minutes, those born to mothers with serum Cr concentrations greater than 1.0 mg/dL, and those with missing data in any stage of the repeatedly measured biomarkers. None of the infants enrolled in this study had any major congenital anomalies. Finally, 36 infants whose renal biomarkers were recorded in the four postnatal age-specific stages were included. This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Keimyung University Dongsan Medical Center (approval no. 2018-01-041-002).
Antenatal data, including gestational age, BW, delivery mode, antenatal steroid use, premature rupture of membrane, pregnancyinduced hypertension, oligohydramnios, fetal growth restriction, and Apgar scores at 1 and 5 minutes, were investigated. Neonatal outcomes, including bronchopulmonary dysplasia, necrotizing enterocolitis (Bell’s stage II or III) [26], advanced intraventricular hemorrhage (Papil grade III or IV) [27], cystic periventricular leukomalacia, bacterial sepsis, patent ductus arteriosus with treatment, and parenteral nutrition during hospitalization, were also investigated. Bronchopulmonary dysplasia was defined as the need for supplemental oxygen or positive pressure support at 36 weeks postconception [28]. Bacterial sepsis was defined as a positive blood culture with antibiotic treatment.
Blood samples were collected at birth from the umbilical cord in the delivery room. Other blood samples were collected from peripheral veins for routine blood screening tests performed during hospitalization. Sera, separated from blood by centrifugation at 1,000 ×g for 10 minutes, was used to measure Cr and CysC levels. As all urine samples were collected with a urine bag for 3 hours, it was difficult to simultaneously obtain urine and blood samples. However, all urine samples were collected within 24 hours after the collection of blood samples. After each urine sample was centrifuged at 500 ×g for 5 minutes, the supernatant was used for measuring urine Cr. Concentrations of serum and urine Cr were determined by the kinetic Jaffe method [29] using an ADVIA 2400 chemistry analyzer (Siemens Healthcare Diagnostics, Erlangen, Germany). Serum CysC was measured with a particle-enhanced immunonephelometric assay using a BNII nephelometer (Siemens Healthcare Diagnostics, Deerfield, IL, USA). Urinary NGAL was measured using chemiluminescent microparticle immunoassay on an ARCHITECT i2000SR system (Abbott Diagnostics, Abbott Park, IL, USA). To eliminate the bias that might be introduced by hydration status, urinary NGAL should be expressed as a ratio relative to the urine Cr concentration [30]. Therefore, we adjusted the urinary NGAL ratio according to the urine Cr concentration.
Demographics were analyzed using descriptive statistics. Continuous variables were expressed as mean±standard deviation, and categorical variables were expressed as numbers and percentages. Associations between renal biomarkers and postconceptional age were assessed using Pearson’s correlation coefficients. Results with P-values less than 0.05 were considered statistically significant. The software package IBM SPSS Statistics version 25 (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA) was used.
Biomarkers measured in each infant were divided into four groups according to postnatal age. Because biomarkers were repeatedly measured during hospitalization, estimates of mean values of renal biomarkers in the four groups were calculated using repeated-measures analysis of variance (ANOVA). Post hoc comparisons were performed using Duncan’s method, and significance was accepted when the P-value was less than 0.05. This statistical analysis was performed using SAS version 9.4 (SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA).
Table 1 shows the characteristics of enrolled infants. The mean gestational age was 27.8±0.3 weeks, and the mean BW was 1,063± 36 g. The incidences of oligohydramnios and fetal growth restriction were 8.3% (3/36) and 11.1% (4/36), respectively. In terms of neonatal characteristics, the incidences of bacterial sepsis, patent ductus arteriosus with treatment, antibiotic treatment during hospitalization, and parenteral nutrition during hospitalization were 16.7% (6/36), 13.9% (5/36), 69.4% (25/36), and 91.7% (33/ 36), respectively.
Figure 1 shows the correlation curves between renal biomarkers and postconceptional age. For samples measured at birth (Figure 1A-C), serum CysC (r=–0.358, P=0.032) and urinary NGAL/Cr ratio (r=–0.522, P=0.001) were negatively correlated with gestational age, whereas serum Cr (r=0.148, P=0.390) was not. In addition, for all samples measured (Figure 1D-F), serum CysC (r=–0.209, P=0.012), urinary NGAL/Cr ratio (r=–0.536, P<0.001), and serum Cr (r=–0.311, P<0.001) were negatively correlated with postconceptional age. However, Pearson’s correlation coefficient for urinary NGAL/Cr ratio was higher than that for serum CysC.
Table 2 shows the mean values of renal biomarkers between four postnatal age-specific stages. Using repeated-measures ANOVA, serum Cr levels were found to be significantly higher in stage II than in stage III and IV, and higher in stage III than in stage IV. Meanwhile, the urinary NGAL/Cr ratio in group IV was significantly different from those in groups I to III. However, serum CysC levels showed no significant differences in any of the four stages.
In the current study, we compared new emerging renal biomarkers according to postconceptional age in VLBW infants. Urinary NGAL/Cr ratio at >28 days postnatally seems to be more affected by postconceptional age than serum CysC.
Preterm infants have fewer functional nephrons and exhibit slower progression in renal maturation after birth [31,32]. Serum Cr at birth does not reflect neonatal but maternal Cr [11-13,33]. To reduce the statistical bias in renal biomarkers, we excluded infants born to mothers with serum Cr concentrations greater than 1.0 mg/ dL. Meanwhile, there is no correlation between maternal and umbilical cord blood CysC [33-35]. There is a significant inverse correlation between urinary NGAL and gestational age at birth [22,36,37]. In the current study, urinary NGAL/Cr ratio and serum CysC concentrations at birth were correlated with postconceptional age, but serum Cr levels at birth were not.
According to a systemic review involving 10 studies, serum CysC was affected by gestational age [35]. In addition, Lee et al. [38] also reported that serum CysC concentrations in term and preterm infants were dependent on both gestational and postconceptional ages. In the current study, serum CysC was weakly correlated with postconceptional age in VLBW infants, which may be due to altered renal development. However, using repeated-measures ANOVA, serum CysC showed no significant differences in any of the four postnatal age-specific stages. These findings imply that serum CysC was less sensitive to postnatal age-related changes in VLBW infants, although the renal development of each infant is different according to gestational age. Additional research is needed to determine whether serum CysC in VLBW infants may be used as an independent indicator for predicting renal injury.
Urinary NGAL in VLBW infants was inversely related to gestational age, but not with postnatal age in a repeated-measures model [22]. Parravicini et al. [39] also reported no correlation between urinary NGAL and postnatal age in VLBW infants without risk factors for renal impairment. Since urinary NGAL levels might be confounded by hydration state and urine output, urinary NGAL should be expressed as a ratio relative to the urine Cr concentration [24,30]. In our previous study, the urinary NGAL/Cr ratio was negatively correlated with gestational and postnatal ages [25]. In the current study, the urinary NGAL/Cr ratio also negatively correlated with the postconceptional age, reflecting renal development according to gestational age. Serum Cr, including all data, also negatively correlated with postconceptional age. In particular, a significant change was found in postnatal age-specific stages using repeated-measures ANOVA. Except for serum Cr at birth, which might be influenced by maternal Cr, significant differences were also observed in the comparison of mean values of serum Cr between the postnatal age-specific stages. These results of urinary NGAL/Cr ratio and serum Cr may indicate improvement in renal function according to renal maturation after birth. Considering the postnatal age-related changes in urinary NGAL/Cr ratio and serum Cr, their absolute values seem unreasonable to be clinically used as an index for predicting renal injury in VLBW infants.
Renal injury is associated with renal development as well as postnatal risk factors, including perinatal events, sepsis, and nephrotoxic medication [8]. In particular, more than 80% of VLBW infants are exposed to nephrotoxic medication during NICU hospitalization [6,7]. In this study, antibiotic exposure occurred in 75% of the enrolled infants, the majority of whom were exposed within 7 days of age. The elevation of serum Cr and urinary NGAL/ Cr ratio at 3 to 7 days postnatally might be a result of antibiotic treatment. However, this assumption is inconclusive as the renal biomarkers were not compared before and after antibiotic use.
Despite the important implications of our findings, our study has several limitations. First, we did not consider the possibility of renal injury following the administration of antibiotics and nephrotoxic medication during hospitalization, although these drugs are known risk factors of renal injury. More detailed studies in VLBW infants with no nephrotoxic medication during hospitalization are needed. Second, we compared renal biomarkers by dividing them into four groups according to postnatal age after birth. For more accurate comparisons based on postconceptional age, prospective studies based on postconceptional age after birth are needed. Third, blood and urine samples were not simultaneously collected, although urine samples were evaluated within 24 hours after blood collection. Finally, serum Cr was measured by the Jaffe method with the possibility of interference from bilirubin or hemolysis in this study population [29], and the likelihood of being affected by maternal Cr levels for the first few days after birth. Thus, further studies using larger cohorts of VLBW infants are needed to evaluate renal biomarkers for the early detection of renal injury.
In conclusion, although urinary NGAL/Cr ratio and serum CysC were negatively correlated with postconceptional age considering renal development, serum CysC showed no significant differences in any of the four postnatal age-specific stages. Urinary NGAL/Cr ratio at >28 days postnatally seems to be more affected by postconceptional age than serum CysC in VLBW infants. When serum CysC and urinary NGAL/Cr ratio were evaluated to assess renal function in VLBW infants, the correlation between these renal biomarkers and postconceptional age was reflected.
ARTICLE INFORMATION
Figure 1.
Correlation between renal biomarkers and postconceptional age in samples at birth (A, B, C) and all other samples (D, E, F). Abbreviations: CysC, cystatin C; NGAL, neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin; Cr, creatinine.
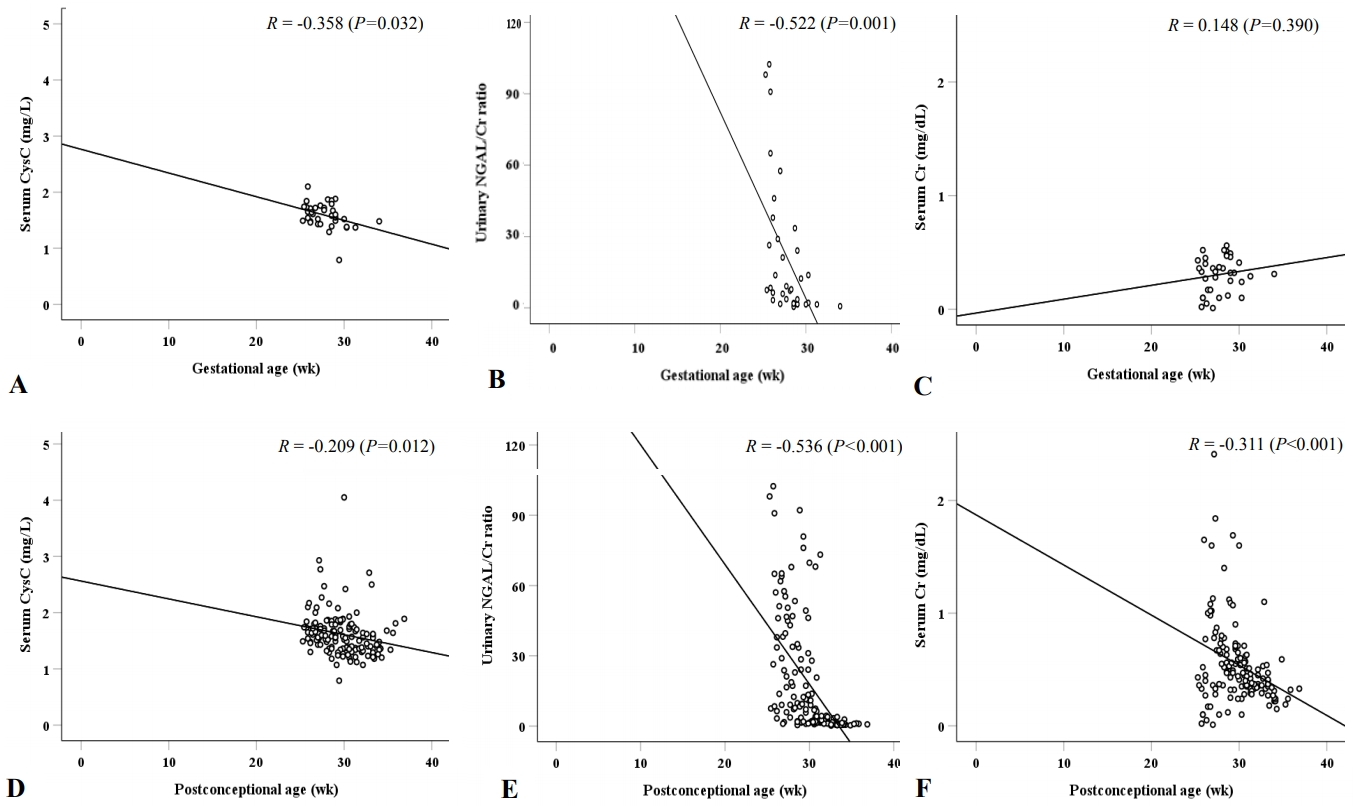
Table 1.
Characteristics of Enrolled Infants (n=36)
Table 2.
Comparison of Mean Values of Renal Biomarkers in the Four Postnatal Age-Specific Stages Using Repeated-Measures Analysis of Variance
| Variable | Stage I | Stage II | Stage III | Stage IV | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Serum CysC (mg/L) | 1.59±0.22 | 1.64±0.36 | 1.70±0.55 | 1.51±0.35 | 0.119 |
| Urinary NGAL/Cr ratio | 20.85±28.53* | 27.89±23.07* | 21.45±26.80* | 4.72±11.58† | <0.001 |
| Serum Cr (mg/dL) | 0.31±0.16* | 0.85±0.39† | 0.64±0.40‡ | 0.38±0.17* | <0.001 |
REFERENCES
1. Askenazi DJ, Griffin R, McGwin G, Carlo W, Ambalavanan N. Acute kidney injury is independently associated with mortality in very low birthweight infants: a matched case-control analysis. Pediatr Nephrol 2009;24:991–7.


2. Koralkar R, Ambalavanan N, Levitan EB, McGwin G, Goldstein S, Askenazi D. Acute kidney injury reduces survival in very low birth weight infants. Pediatr Res 2011;69:354–8.


3. Hinchliffe SA, Sargent PH, Howard CV, Chan YF, van Velzen D. Human intrauterine renal growth expressed in absolute number of glomeruli assessed by the disector method and Cavalieri principle. Lab Invest 1991;64:777–84.

4. Stelloh C, Allen KP, Mattson DL, Lerch-Gaggl A, Reddy S, El-Meanawy A. Prematurity in mice leads to reduction in nephron number, hypertension, and proteinuria. Transl Res 2012;159:80–9.


5. Veille JC, McNeil S, Hanson R, Smith N. Renal hemodynamics: longitudinal study from the late fetal life to one year of age. J Matern Fetal Investig 1998;8:6–10.

6. Rhone ET, Carmody JB, Swanson JR, Charlton JR. Nephrotoxic medication exposure in very low birth weight infants. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med 2014;27:1485–90.


7. Barhight M, Altaye M, Gist KM, Isemann B, Goldstein SL, Akinbi H. Nephrotoxic medications and associated acute kidney injury in very low birth weight infants. J Clin Nephrol Res 2017;4:1070.


8. Selewski DT, Charlton JR, Jetton JG, Guillet R, Mhanna MJ, Askenazi DJ, et al. Neonatal acute kidney injury. Pediatrics 2015;136:e463–73.


9. Filler G, Browne R, Seikaly MG. Glomerular filtration rate as a putative ‘surrogate end-point’ for renal transplant clinical trials in children. Pediatr Transplant 2003;7:18–24.


10. Askenazi DJ, Ambalavanan N, Goldstein SL. Acute kidney injury in critically ill newborns: what do we know?: what do we need to learn? Pediatr Nephrol 2009;24:265–74.



11. Gordjani N, Burghard R, Leititis JU, Brandis M. Serum creatinine and creatinine clearance in healthy neonates and prematures during the first 10 days of life. Eur J Pediatr 1988;148:143–5.


12. Iacobelli S, Bonsante F, Ferdinus C, Labenne M, Gouyon JB. Factors affecting postnatal changes in serum creatinine in preterm infants with gestational age <32 weeks. J Perinatol 2009;29:232–6.


13. Filler GM. The challenges of assessing acute kidney injury in infants. Kidney Int 2011;80:567–8.


14. Gallini F, Maggio L, Romagnoli C, Marrocco G, Tortorolo G. Progression of renal function in preterm neonates with gestational age < or = 32 weeks. Pediatr Nephrol 2000;15:119–24.

15. Delanaye P, Ebert N. Assessment of kidney function: Estimating GFR in children. Nat Rev Nephrol 2012;8:503–4.



16. Demirel G, Celik IH, Canpolat FE, Erdeve O, Biyikli Z, Dilmen U. Reference values of serum cystatin C in very low-birthweight premature infants. Acta Paediatr 2013;102:e4–7.


17. Elmas AT, Tabel Y, Elmas ON. Reference intervals of serum cystatin C for determining cystatin C-based glomerular filtration rates in preterm neonates. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med 2013;26:1474–8.


18. Kristensen K, Strevens H, Lindstrom V, Grubb A, Wide-Swensson D. Increased plasma levels of beta2-microglobulin, cystatin C and beta-trace protein in term pregnancy are not due to uteroplacental production. Scand J Clin Lab Invest 2008;68:649–53.

19. Dharnidharka VR, Kwon C, Stevens G. Serum cystatin C is superior to serum creatinine as a marker of kidney function: a meta-analysis. Am J Kidney Dis 2002;40:221–6.


20. Mishra J, Ma Q, Prada A, Mitsnefes M, Zahedi K, Yang J, et al. Identification of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin as a novel early urinary biomarker for ischemic renal injury. J Am Soc Nephrol 2003;14:2534–43.


21. Mori K, Lee HT, Rapoport D, Drexler IR, Foster K, Yang J, et al. Endocytic delivery of lipocalin-siderophore-iron complex rescues the kidney from ischemia-reperfusion injury. J Clin Invest 2005;115:610–21.



22. Lavery AP, Meinzen-Derr JK, Anderson E, Ma Q, Bennett MR, Devarajan P, et al. Urinary NGAL in premature infants. Pediatr Res 2008;64:423–8.


23. Zappitelli M, Washburn KK, Arikan AA, Loftis L, Ma Q, Devarajan P, et al. Urine neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin is an early marker of acute kidney injury in critically ill children: a prospective cohort study. Crit Care 2007;11:R84.



24. Devarajan P. NGAL for the detection of acute kidney injury in the emergency room. Biomark Med 2014;8:217–9.



25. Shin SY, Ha JY, Lee SL, Lee WM, Park JH. Increased urinary neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin in very-low-birth-weight infants with oliguria and normal serum creatinine. Pediatr Nephrol 2017;32:1059–65.


26. Bell MJ, Ternberg JL, Feigin RD, Keating JP, Marshall R, Barton L, et al. Neonatal necrotizing enterocolitis: therapeutic decisions based upon clinical staging. Ann Surg 1978;187:1–7.



27. Papile LA, Burstein J, Burstein R, Koffler H. Incidence and evolution of subependymal and intraventricular hemorrhage: a study of infants with birth weights less than 1,500 gm. J Pediatr 1978;92:529–34.


29. Osberg IM, Hammond KB. A solution to the problem of bilirubin interference with the kinetic Jaffé method for serum creatinine. Clin Chem 1978;24:1196–7.


30. Waikar SS, Sabbisetti VS, Bonventre JV. Normalization of urinary biomarkers to creatinine during changes in glomerular filtration rate. Kidney Int 2010;78:486–94.



31. Sutherland MR, Gubhaju L, Moore L, Kent AL, Dahlstrom JE, Horne RS, et al. Accelerated maturation and abnormal morphology in the preterm neonatal kidney. J Am Soc Nephrol 2011;22:1365–74.



33. Kuppens M, George I, Lewi L, Levtchenko E, Allegaert K. Creatinaemia at birth is equal to maternal creatinaemia at delivery: does this paradigm still hold? J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med 2012;25:978–80.


34. Cataldi L, Mussap M, Bertelli L, Ruzzante N, Fanos V, Plebani M. Cystatin C in healthy women at term pregnancy and in their infant newborns: relationship between maternal and neonatal serum levels and reference values. Am J Perinatol 1999;16:287–95.


35. Kandasamy Y, Smith R, Wright IM. Measuring cystatin C to determine renal function in neonates. Pediatr Crit Care Med 2013;14:318–22.


36. Huynh TK, Bateman DA, Parravicini E, Lorenz JM, Nemerofsky SL, Sise ME, et al. Reference values of urinary neutrophil gelatinase- associated lipocalin in very low birth weight infants. Pediatr Res 2009;66:528–32.



37. Gubhaju L, Sutherland MR, Horne RS, Medhurst A, Kent AL, Ramsden A, et al. Assessment of renal functional maturation and injury in preterm neonates during the first month of life. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 2014;307:F149–58.


-
METRICS

-
- 0 Crossref
- 3,969 View
- 77 Download
- Related articles in NM
-
The Risk Factors of Periventricular Leukomalacia among Very Low Birth Weight Infants2020 May;27(2)






